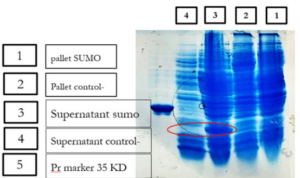
Fig.6: Confirmation of cytoplasmic expression of SUMO-VEvhh10 with the help of sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. The samples examined include, from right to left, 1 – sedimentation of transforming bacteria and induced with IPTG after their lysis, 2 – Transformed, untransformed and post-lysis bacterial sediments, 3 – Transformed and induced bacterial supernatants after lysis, 4 – Untransformed and induced bacterial supernatants after lysis, 5 – 35 kDa molecular weight protein as a protein marker.
2024-10-03 | | |Fig.6: Confirmation of cytoplasmic expression of SUMO-VEvhh10 with the help of sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. The samples examined include, from right to left, 1 – sedimentation of transforming bacteria and induced with IPTG after their lysis, 2 – Transformed, untransformed and post-lysis bacterial sediments, 3 – Transformed and induced bacterial supernatants after lysis, 4 – Untransformed and induced bacterial supernatants after lysis, 5 – 35 kDa molecular weight protein as a protein marker.
(ISSN - Online)
2959-8591