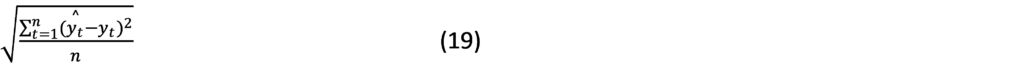INTRODUCTION
Although coins and banknotes are in issues for decades, there is no agreement amongst economists on what is the theoretically optimal denomination structure of a currency [1]. Two components are usually used to identify any denomination structure, those being the structure boundary and the series within the boundary. The structure boundary includes determining the lowest coin value, the highest banknote value and the transition between coins and banknotes. The series inside the boundary includes the number of coins, banknotes, and total number of denominations [2]. Determining the optimal denomination structure of a currency is a daunting task. It involves ensuring the efficiency of the structure, its cost effectiveness and its balance in terms of having a proper mix of the various denominations [3] [4]. To ensure this task is well handled, central banks need to closely monitor the evolving changes (technology, security issues, high inflation..etc) and timely respond to them [5]. Empirically, [6] proposed the D-Metric model to determine the denomination structure of the currency. The model utilizes the relationship between the average daily wage level (D) and the denominations of the currency to identify the coins on the lower scale that need to be withdrawn from circulation, the boundary point between coins and banknotes, and the appropriate timing for the introduction of higher banknotes [7]. This study uses the D-Metric model to analyze changes in the denomination structure of the Syrian Pound between 1997 and 2022. The choice of the period is to capture the last three changes in terms of introducing a higher banknote in Syria. The study was motivated by the scarcity of previous research on the optimal denomination structure in general and in Syria, in particular. The study was further motivated by the public attention that accompanied the introduction of the SP5000 and the rumors regarding the potential issuance of the SP10000. The aim of this study is twofold. First, to analyze the denomination structure of the Syrian Pound and to verify whether the introduction of the last three high denomination banknotes was justified from the D-Metric model point of view. Second, to analyze whether a higher banknote should be introduced. The study contributes to the literature on the optimal denomination structure as it is the first that analyzes the denomination structure of the Syrian currency using the D-Metric model. The findings of the study have empirical implications for the Central Bank and the public in Syria. They will enable recommending the denomination of the higher banknote that should be issued and the timing of this issuance. The remainder of the study is organized as follows: Section one sheds light on the currency structure in Syria. Section two explains the D-Metric model. Section three analyzes the denomination structure in Syria using the D-Metric model. Section four concludes the paper.
The Currency Structure in Syria
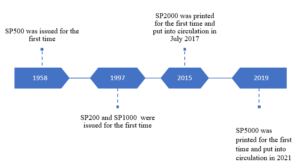
The monetary authorities and denomination structure in Syria passed through several historical landmarks. Below is a brief highlight of this main historical changes. In the era of the French Mandate, the Bank of Syria supervised the process of issuing the currency. The name of the bank changed later on during that period to become the Bank of Syria and Lebanon. After gaining independence, the Bank of Syria and Lebanon continued on issuing the currency in both Syria and Lebanon. However, it was replaced later on by the Syrian Institute for Issuing Money. In 1953 the Legislative Decree No. /87/ was issued [8]. The Decree defined the basic monetary system in Syria and established a Council for Money and Credit to take on the tasks of the Central bank. The Central Bank of Syria did not officially start working until 1/8/1956. Below is a review of the development of the currency structure since the Central Bank of Syria became responsible for supervising the issuance of the Syrian Pound, the official currency in the Syrian Arab Republic. Figures (1) and (2) below show the development of the currency structure after the Central Bank of Syria became responsible for issuing the Pound. As per the structure of coins, after its establishment, the Central Bank of Syria continued to issue coins in the denominations of 2, 5, 25 and 50 Piasters and one Pound that previously existed. In 1960, a new coin in the denomination of 10 Piasters was issued for the first time. As shown in Figure (1), the structure of the coins remained unchanged until 1995, when new coins in the denomination of 25 Pounds were issued. In 1996, new coins in the denominations of 2, 5 and 10 Pounds were issued for the first time. In the same year, coins in the denominations of 2, 5 and 10 Piasters were withdrawn from circulation. In 2004, coins in the denominations of 25 and 50 Piasters were withdrawn from circulation. At the end of 2018, the highest denomination of coins, 50 Pounds, was issued [9]. With regard to the structure of banknotes, the Central Bank of Syria continued to issue banknotes in the denominations of 1, 5, 10, 25, 50 and 100 Pounds which previously existed. In 1958 a new banknote in the denomination of SP500 was issued for the first time. As Figure (2) reveals, the structure of banknotes remained unchanged until year 1997, when banknotes in the denominations of SP200 and SP1000 were issued for the first time. More than ten years in the Syrian crisis, which started in 2011, caused a massive economic destruction to the Syrian economy. The Syrian Pound which had a pre-crisis exchange rate on the average of USD1= SP45 gradually depreciated to exceed USD1= SP3800 in the black market. The depreciation of the Syrian Pound and the high inflation that Syria was facing triggered many questions regarding the necessity of issuing higher banknotes. In 2015, with the annual inflation rate reaching an average of 38.46%, the SP2000 note was printed for the first time. It was put into circulation in July 2017 when the annual inflation rate was 14.48% [10]. Recently, in 2021, a new note in the denomination of SP5000 was put into circulation. The 5000 note was printed in 2019 when the annual inflation rate was, on average, 13.42%] [10]. According to the official releases of the Central Bank of Syria, the SP5000 note was printed to meet the trading needs of the public in a manner that ensures facilitation of monetary transactions and reduces the cost and intensity of dealing in banknotes. The Central Bank reported that the current economic changes, and the significant rise in prices that started in the last quarter of 2019 and continued during 2020, made the timing appropriate for putting the SP5000 into circulation [10]. Following the issuance of the SP5000, there was a public debate on whether the SP10000 needs to be issued and put into circulation or whether it is premature to do so.
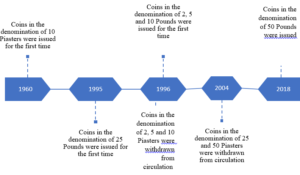 Figure (1): Timeline of the development of the coin structure in Syria
Figure (1): Timeline of the development of the coin structure in Syria
The following section introduces the D-Metric model that will be used to analyze the changes in the currency structure in Syria since the introduction of the three highest banknotes (SP1000, SP2000, and SP5000).
MATERIALS AND METHODS
The D-Metric model
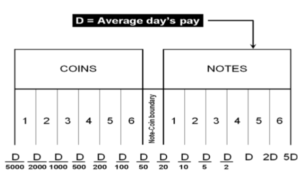
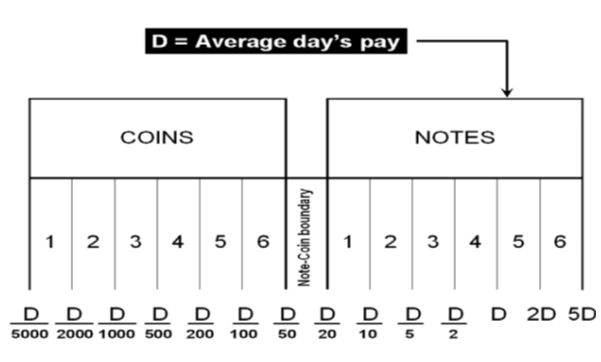
Determining the optimal denomination structure includes identifying the structure boundary and the series within the boundary. That is to say, identifying the lowest coin value, the highest banknote value and the transition between coins and banknotes along with the number of coins, banknotes, and total number of denominations inside the boundary. The spacing of the denominations in most countries is based on either a binary-decimal triplets system (1-2-5) or a fractional-decimal triplets system (1-2.5-5) [2]. Syria is amongst countries that adopted a mix of the two systems. It has six denominations of coins (1, 2, 5, 10, 25, and 50) and seven denominations of banknotes (50, 100, 200, 500, 1000, 2000, 5000). The denomination of (5, 10, and 25) banknotes are legal tender although they are not issued any more by the Central Bank. As can be seen, the denominations (10, 25 and 50) follow the (1-2.5-5) system while the rest of the denominations follow the (1-2-5) system. Trying to figure out the optimal denomination structure, [6] used data from sixty currency-issuing authorities around the world. They documented a consistent relationship between the average daily pay (D) in a country and its currency structure. They reported that in most of the examined countries, the boundary denomination between coins and banknotes is located between D/50 and D/20. The top and lowest denominations are around five folds of the average daily pay (5D) and 5000 parts of the average daily pay (D/5000), respectively [12]. As shown in Figure (3), the model assumes that there are six denominations of coins and six denominations of banknotes along with one denomination at the boundary between coins and banknotes. The model can be used to advise when a modification on the denomination structure is needed. This includes the modification of the lowest-highest denominations and the transition between coins and banknotes [2]. The D-Metric model, however, is subject to several limitations. First, it is a practical method that lacks a theoretical base. Second, it ignores other factors that should be taken into consideration when determining the denomination structure of a currency. This includes, the costs associated with economic agents and users’ preferences, including payment habits [13] [14] [15]. The model also ignores the fact that payment habits, culture and wealth holding might differ across countries and could vary, within the same country, over time. In addition, the model fails to take into account the durability of monetary items and their costs when determining the boundary point between coins and notes [2]. Despite being subject to several limitations, the simplicity of the D-Metric model makes it used as a guideline to the re-denomination of currencies and it has been successfully applied in a wide range of countries around the globe [12] [16] [17]. The following section will utilize the D-Metric model to analyze the denomination structure in Syria between 1997-2022.
RESULTS
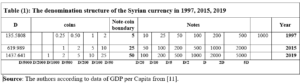
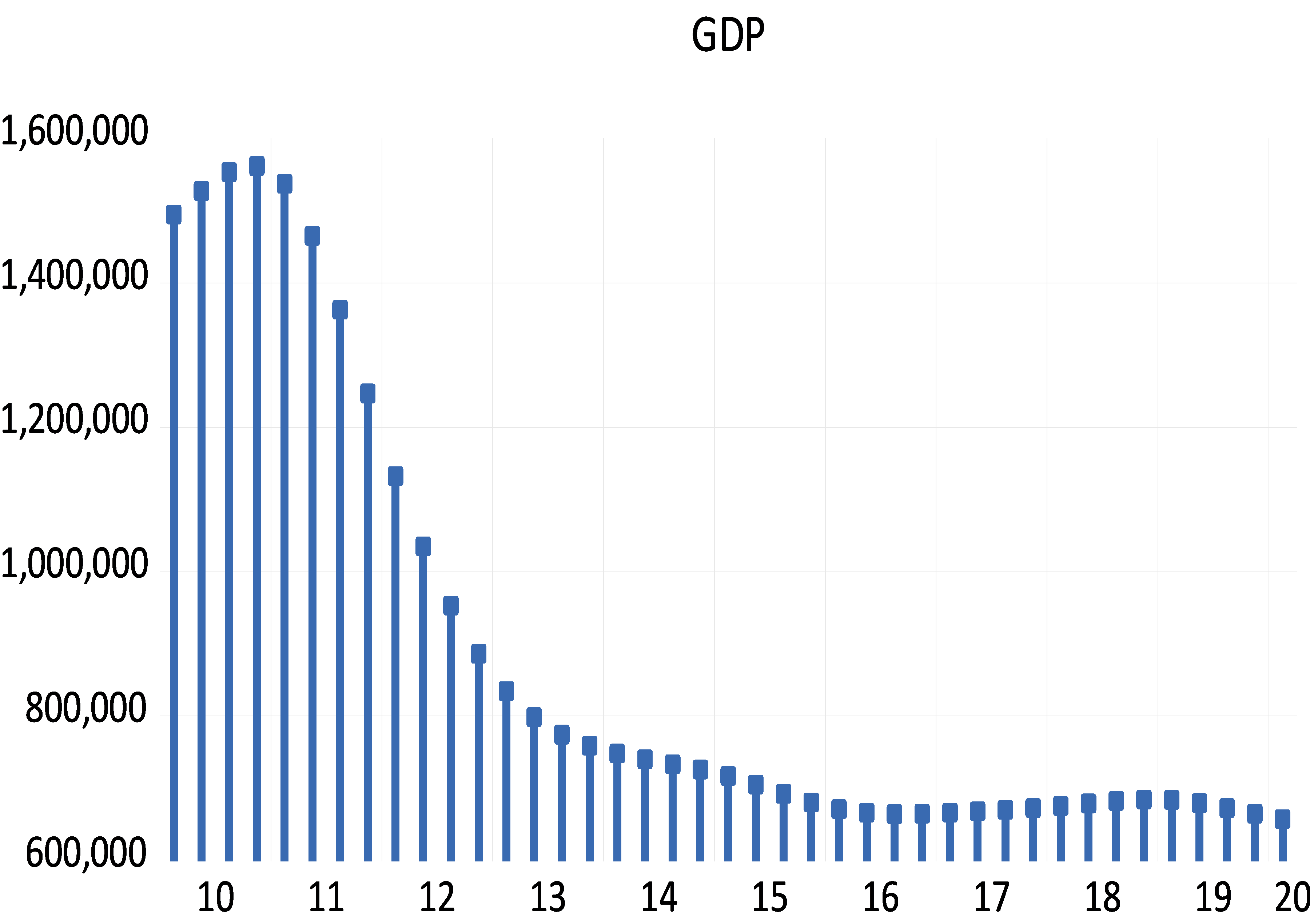
As Figure (2) indicated, bigger banknotes were issued in 1958, 1997, 2015 and 2019. Our analysis of the denomination structure in Syria is limited to years 1997, 2015 and 2019. Year 1997 was chosen as it experienced the last issuance of a higher banknote, the SP1000, prior to the eruption of the Syrian crisis.[1] Years 2015 and 2019 were chosen as they are the years in which the two higher banknotes, the SP2000 and SP5000, were issued. Years between 1997 and 2015 were not examined as there are no issuance of higher banknotes in these years. As highlighted earlier, the D-Metric model relates the average daily wage level to the denomination structure of the currency. Due to data availability issues, the nominal GDP per capita per day was used as a proxy for the average daily pay (D in the D-Metric diagram). The daily GDP per capita was adopted by many authors on their application of the D-Metric model [2] [12]. Table (1) reveals the value of D and the denomination structure in each of the examined years.
DISCUSSION
Starting with year 1997, the D-Metric model suggests that the lowest useful coin should be between SP0.02 (D/5000) and SP0.067 (D/2000). The note-coin boundary should be between SP2.7 (D/50) and SP6.7 (D/20), suggesting that the higher coin should be SP5, which can be either a coin or a banknote. The largest banknote suggested by the model is the SP500 banknote which falls between SP271 (2D) and SP677 (5D). Table (1), however, reveals mismatches between the theoretical denomination structure suggested by the D-Metric model and the actual structure in year 1997. To be more specific, the lowest coin, 25 Piasters (SP0.25), lies between D/1000 and D/500 instead of D/5000 and D/2000, as suggested by the model, and the highest coin is SP25 instead of SP5.[2] In addition, the SP10 and SP25 exist in coins and banknotes whereas the model predicts that the note-coin boundary should be SP5. Another mismatch with the D-Metric model is the existence of the SP1000 banknote whereas, according to the model, the highest banknote should be SP500 (between 271 and 677.9). Accordingly, based on the D-Metric analysis of the currency structure in year 1997, one can conclude that the structure is not the optimal one and that the introduction of the SP1000 was premature and should have been postponed until year 2005 when 5D was equal to SP1124.219. The structure recommended by the D-Metric model changes in 2015 in comparison to that in 1997. As shown in Table (1), the SP25 got pushed into the note-coin boundary whereas the SP5 and the SP10 fell into the coin category. Furthermore, the SP2000 banknote became the largest useful banknote. Unlike the mismatch in year 1997, it seems that the currency structure in 2015 complies with the theoretical denomination structure suggested by the D-Metric model in this year. The highest coin in circulation in 2015, SP25, falls into the note-coin boundary (D/20=619.989/20=30.999) and (D/50=619.989/50=12.399) and the highest banknote, SP2000, falls between (2D=2*619.989=1239.978) and (5D=5*619.989=3099.945). Therefore, it was appropriate, then, to issue the SP2000 banknote in this year. In fact, it was even appropriate to issue it in 2014, when D was SP471.6 (2D=943 and 5D=2358) [11]. Since the SP2000 was printed in 2015 but not put into circulation until 2017, the analysis requires examining whether it was put into circulation on the right timing. Knowing that in year 2017, D was equal to SP1053.99, the SP2000 falls outside what is suggested by the model (2D=2107.98 and 5D=5269.95). Accordingly, the delay in introducing the SP2000 into the market was inconsistent with the denomination structure suggested by the D-Metric model. In fact, the D-Metric analysis suggests that the SP5000 banknote could have been put into circulation in 2017 and not just the SP2000. As can be seen from Table (1) the structure recommended by the D-Metric model changes in 2019 in comparison to that in 2015. The SP50 got pushed into the note-coin boundary whereby the SP25 fell into the coin category. Furthermore, the SP5000 banknote became the largest useful banknote (lying between 2D=1437.641*2=2875.28 and 5D=1437.641*5=7188.2). The Table also reveals that the lowest useful coins for this year, SP1 and SP2, fall within D/2000-D/1000 and D/1000-D/500, respectively. The lowest useful banknote, SP50, falls into the note-coin boundary (between (D/50=1437.641/50=28.75) and (D/20=1437.641/20=71.88)). This means that the decision to issue the SP50 coin was appropriate. Adhering to the 1-2-5 system of spacing, the next useful banknotes would be 100, 200, 500, 1000, 2000, 5000 according to the model. Indeed, those are the currencies that are actually in circulation in that year. Although it is justified to put the SP5000 banknote in circulation since 2017 as indicated above, the note was not put in circulation until 2021.
Should a higher banknote be put into circulation?
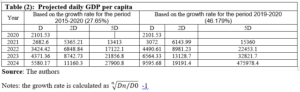
Recently, there are discussions among the public and economists regarding the necessity of issuing a higher banknote (the SP10000 banknote). Issuing higher banknotes has its own advantages and disadvantages. One of the main advantages is the easy handling of transactions as people do not have to carry large quantities of money to do their daily transactions [20]. This is especially important bearing in mind the high reliance on cash and the very low reliance on E payment in Syria. Another advantage is the lower carrying and management expenses, as according to the Central Bank of Korea, issuing the higher denomination allowed a saving of 60 billion won (approximately USD 50,000,000) every year due to reductions in management expenses especially those related to logistic costs [21]. In addition, the higher notes have lower production costs as they are less frequently used and used with more caution than is the case for smaller notes [13]. The higher notes could also help reduce spending as people are less encouraged to buy something if they have to pay one big note than is the case if they are paying with several smaller notes [13]. Issuing higher notes might also protect the national identity of the country by reducing the chances of substituting the domestic currency for other currencies (dollarization) [22]. The major disadvantage of issuing higher banknotes, lies on the inflationary impact of issuing higher notes, which could be a very serious one. As expectations of inflation drive up inflation, the higher note might be followed by higher inflation. The fear is that if the cycle starts, it is not easy to stop it. More precisely, if inflation increases after the issuance of the higher banknote, this might lead to the issuance of a higher note and the cycle goes on. Other disadvantages of issuing a higher note revolves around production costs, susceptibility to forgery and facilitation of drag dealing and illegal activities [23] [24]. To determine whether a higher note, the SP10000, should be issued, we applied the D-Metric model on the daily GDP per capita for the year 2020 where D is equal to SP2101.06 [11]. As highlighted earlier, according to the model the highest note should be between 2D and 5D. This means that the highest note should be between SP 4202.12 and SP10505.3. Accordingly, the D-Metric model suggests that the SP10000 could have been issued and put into circulation since 2020. The high inflation that Syria is still facing makes us in doubts of whether a higher banknote should be issued as the SP10000 might not be enough to meet the needs of the daily transactions. Table (2) reveals the results of applying the D-Metric model on the daily GDP per capita for the year 2021 where D is equal to SP3099.93 [11]. As the table reveals the 2D and 5D are 6199.86 and 15499.65 respectively. This indicates that the 10000 note is enough and no higher note needed to be issued in that year. Unfortunately, no data of the daily GDP per capita for the year 2022 is available to conduct the analysis. To circumvent this issue, we tried to extrapolate the expected growth rate based on the historical growth rate, under two scenarios. In the first scenario, we used the daily GDP per capita in years 2015 and 2021 to calculate the average growth rate for the period.[1] This was then used to project the future daily GDP per capita on the following years. In the second scenario, we assumed that the growth rate on the daily GDP per capita between years 2020 and 2021 would remain unchanged, and we used this growth rate to project the future daily GDP per capita on the following years. Table (2) reveals the results of applying the D-Metric model based on both of the simulated scenarios. As Table (2) reveals, applying the average growth rate for the period 2015-2021 shows that the issuance of the SP20000 could be done in 2023 and should not be pushed beyond 2024. However, applying the aggressive growth rate, the one that is based on the growth rate of years 2020-2021, reveals that the issuance of the SP20000 could be done in 2022 and should not be pushed beyond 2023. The fact that the SP10000 could have been issued and put into circulation since year 2020 and that the SP20000 should not be pushed beyond 2023-2024, indicates that the monetary authorities might have to issue both of the banknotes, 10000 and 20000, at one time or within a short time span. This, however, might have adverse outcomes on the inflation levels that are already high!
CONCLUSION AND RECOMMENDATIONS:
The aim of this study was to analyze the denomination structure of the Syrian Pound between 1997 and 2022 and to examine whether the decisions of issuing the higher banknotes (SP1000, SP2000 and SP5000) were justified based on the D-Metric model predictions. The study also aimed to examine whether higher banknotes (SP10000 and SP 20000) need to be issued and put in circulation and what is the appropriate timing for this. The study was mainly motivated by the recent issuance of higher banknotes in Syria along with expectations of further issuance of higher banknotes. When comparing the denomination structure in the examined period with that suggested by the D-Metric model, the findings revealed that the introduction of the higher note, SP1000, in 1997 was premature and should have been postponed to 2005, however the issuance of the SP2000 was on the right timing. The delay however in putting the SP2000 in circulation was not consistent with the outcomes of the D-Metric model. The SP2000 was put into circulation in 2017 when it was appropriate to issue the SP5000. The findings also reveal that the issuance of the SP5000 in 2019 was consistent with the predictions of the D-Metric model. When examining whether a higher banknote, SP10000, should be issued, the D-Metric model suggests that the SP10000 could have been issued and put into circulation since 2020. The high inflation that Syria is facing now tempted us to examine whether the SP20000 should be issued. To overcome the lack of data on daily GDP per capita after 2021, we used two growth scenarios to simulate the daily GDP per capita for the coming years. The findings indicate that the SP20,000 should not be pushed beyond 2023-2024 the latest. The fact that the issuance of the SP20000 should not be pushed beyond 2023-2024 and that the SP10000 could have been issued and put into circulation since 2020 means that the monetary authorities should not delay the issuance of the SP10000 anymore. Otherwise, the monetary authorities might have to issue the two notes SP10000 and SP20000 at the same timing or within a very short time span. This, however, might have detrimental impact on the public confidence in the currency and might trigger higher and higher levels of inflation. Although the analysis was based on the simple and easy to apply D-Metric model, the popularity of the model among central banks and the cross-country empirical evidence that supported its predictions, allow us to utilize it. The findings obtained when applying the model have important implications to the monetary authorities in Syria. They, the findings, indicate that delaying the issuance of a higher note creates further problems in terms of having to issue a further higher banknote soon, which increases the uncertainty in the market and could create higher inflationary expectations. The findings are also of high importance to the public as finding the optimal currency structure enhances the efficiency of cash payment’s settlement. Despite the important findings of the current study, they should be interpreted with caution due to several reasons. First, as highlighted earlier, the D-metric model relates the average daily pay in an economy and the currency denomination structure, however, it does not take into account other factors that affect the denomination structure. This includes amongst other things, the cost structure and economies of scale associated with the printing and minting of a currency, the presence of extra demand on specific denominations, laws and regulations, public’s perception of inflation, etc. The currency denomination structure of a country is also a function of its past economic and political events which is not taken into account by the D-Metric model [12]. Two areas for future research emerge from this study. First, a multidimensional study that takes into account other factors that could affect the denomination structure is needed to get a better understanding of the suitability of the current and future denomination structures. Second, as issuing higher notes could be a response to the higher levels of inflation, the bidirectional relationship between issuing higher notes and inflation would be very informative to the monetary authorities and the public as very little evidence exists on this area.

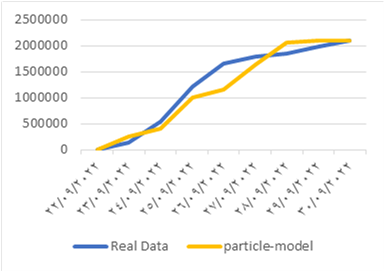

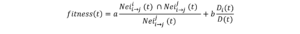
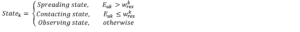

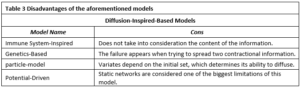



 Our results also show that there are many obstacles that prevent the success of the interlinking between the SRBs and PSBs, the most important of which is the lack of institutionalization of the interdependence process among them.
Our results also show that there are many obstacles that prevent the success of the interlinking between the SRBs and PSBs, the most important of which is the lack of institutionalization of the interdependence process among them.
 Source:
Source: 

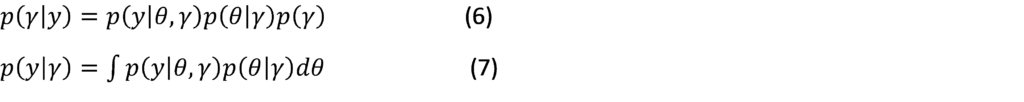
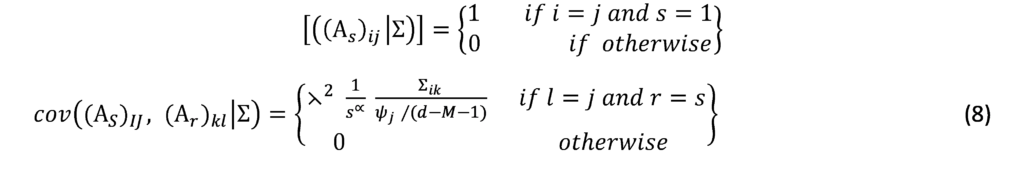
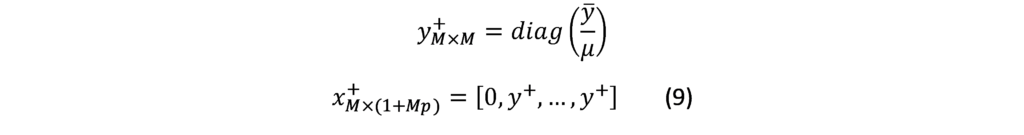
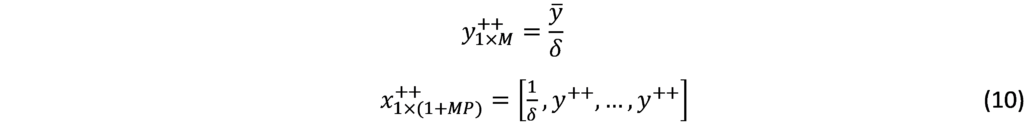
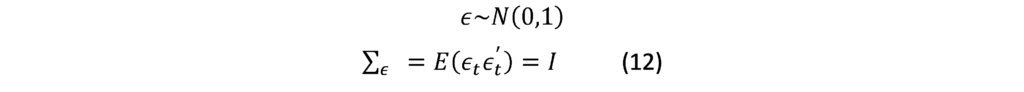
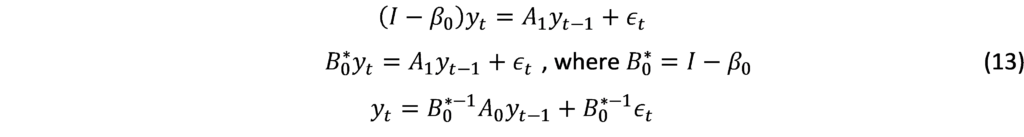
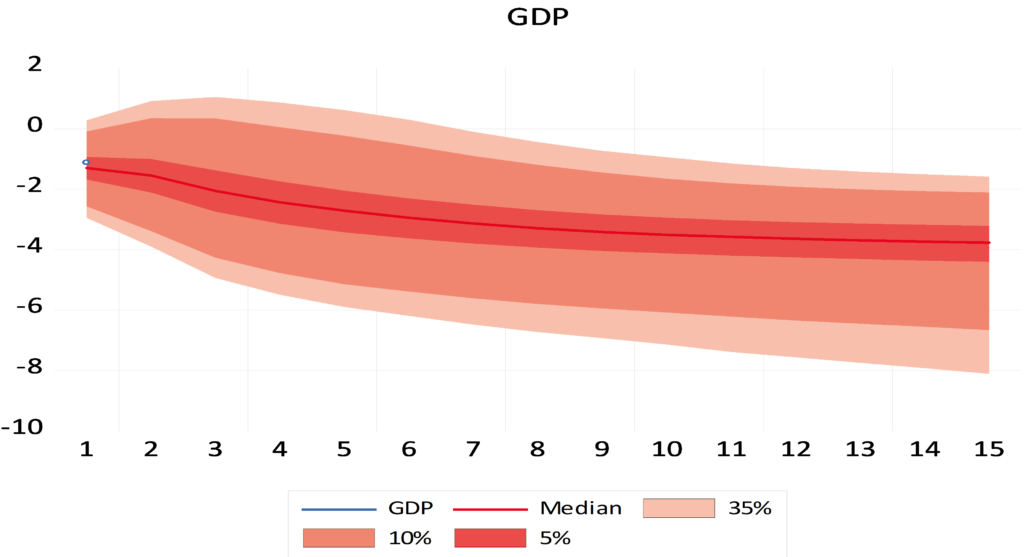
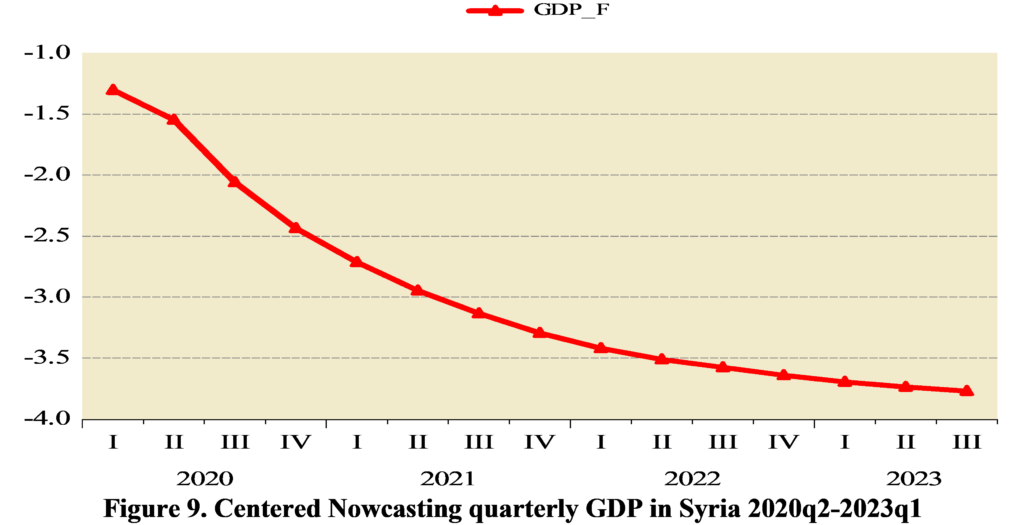
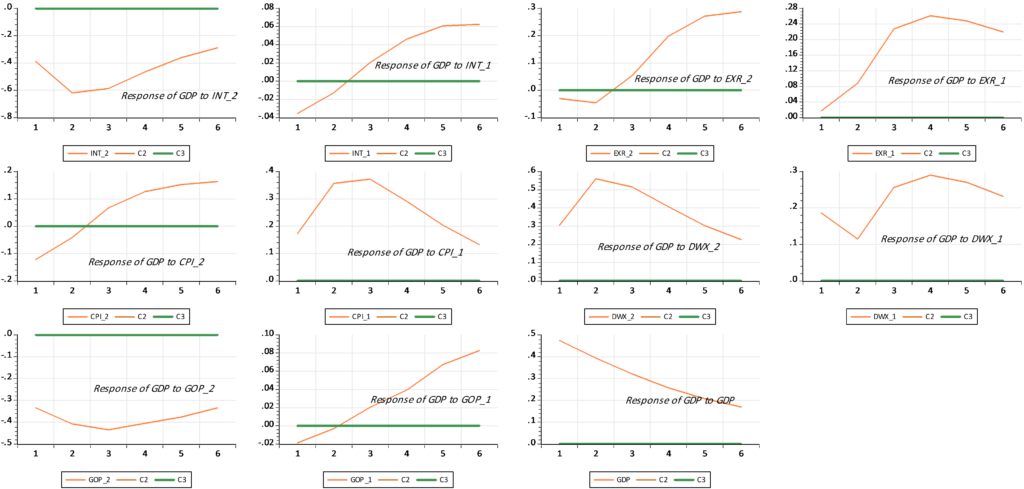
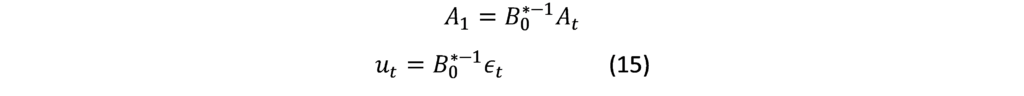 Mixed Frequency VAR
Mixed Frequency VAR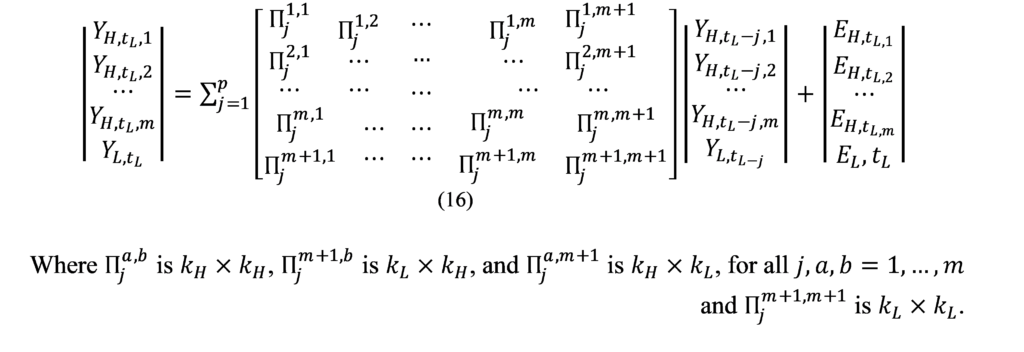
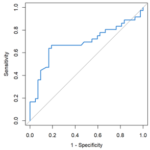
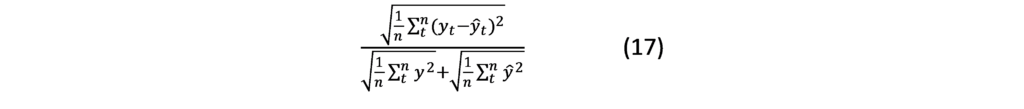 Mean Absolute Error (MAE):
Mean Absolute Error (MAE):